252 resultater fundet
Skip results of view Datahistorier

- Data Story
Bavaria, the German state best known for ‘laptops and lederhosen’, makes open data a priority. With its new Digital Plan, the State Ministry for Digital Affairs aims to motivate Bavarian public administrations to share their open data and thus increase transparency and foster open data reuse. To achieve this aim, it is developing, together with a specialised open data team, a new state-of-the-art...
- Data Story
Recycling is a key element of the European Union’s waste management policy. It aims to contribute to the realisation of a circular economy that maximises the extraction of high-quality resources from waste. The European Green Deal , which serves as the blueprint for a modern, resource-efficient and competitive economy, prioritises the transition towards sustainable practices. In pursuit of this...
- Data Story
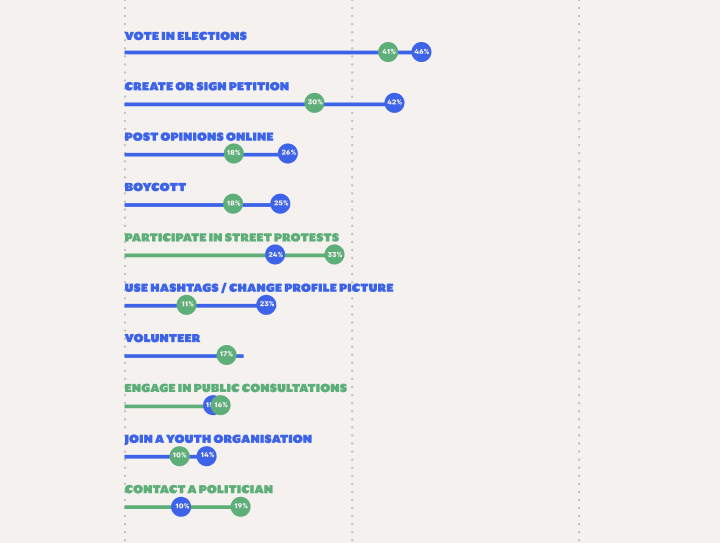
European democracy is strengthened when citizens actively participate in political and civic life. The active involvement of Europe’s young citizens is especially important since the attitudes and opinions of young people foreshadow future trends and developments in society. But how are young people in Europe participating? Are they engaged in civil society? Data can be an essential element to...
- Data Story
This is part of a series of articles showcasing examples of high-value datasets from different thematic categories. High-value datasets are defined by EU law based on their potential to provide essential benefits to society, the environment and the economy. This series aims to help readers find reliable and accurate information from official sources relating to the availability of various high...
- Data Story
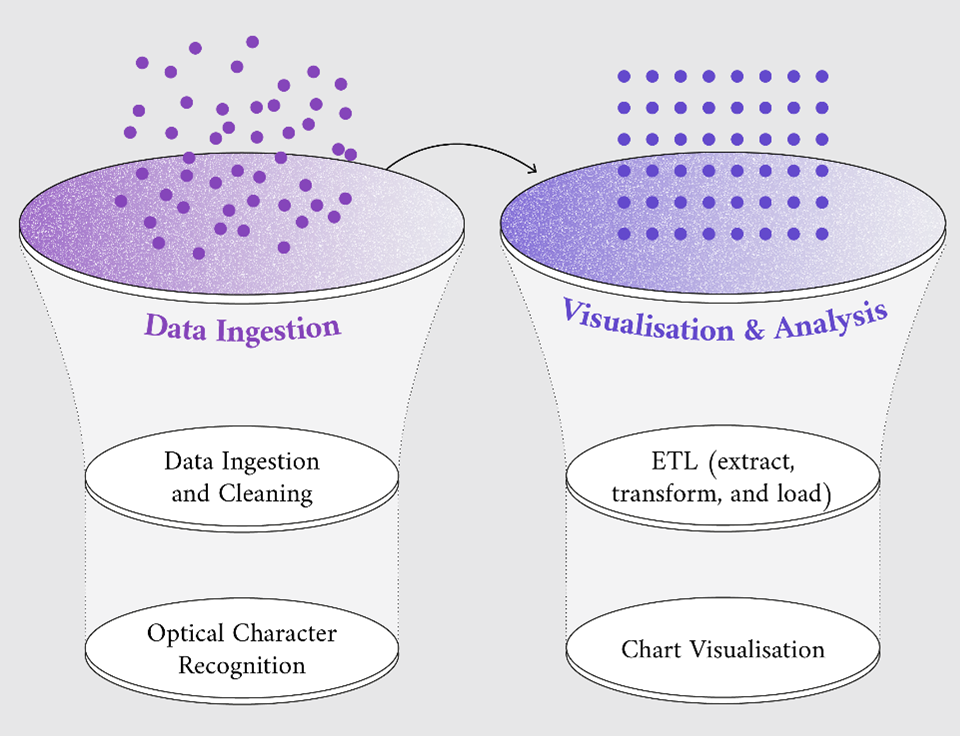
If you are a devoted reader of the data.europa.eu data stories, you have likely come across numerous inspiring examples of open data reuse. Each story illustrates what can be achieved by the best data science practices, by the amazing tools available to us today, and by incredibly effective and beautiful visualisations. Maybe you were also wondering how to create such visualisations yourself and...
- Data Story
This is part of a series of articles showcasing examples of high-value datasets from their different thematic categories. High-value datasets are defined by EU law based on their potential to provide essential benefits to society, the environment and the economy. This series aims to help readers find reliable and accurate information from official sources relating to the availability of various...
- Data Story
Introduction The Open Data Maturity (ODM) report provides an overview of the progress achieved by European countries as they push forward in creating the necessary conditions to make the most of open data. The concept of open data maturity in Europe is considered against four dimensions: quality, portal, policy, and impact. Open data portals are platforms that facilitate data access and reuse...
- Data Story
This is part of a series of articles showcasing examples of high-value datasets from their different thematic categories. High-value datasets are defined by EU law based on their potential to provide essential benefits to society, the environment and the economy. This series aims to help readers find reliable and accurate information from official sources relating to the availability of various...
- Data Story
Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems are complex mathematical models trained on data. These systems are designed to process and analyse large volumes of data with the purpose of recognising patterns and making predictions. AI systems are becoming increasingly accurate and sophisticated due, in part, to advances in the techniques and algorithms used for AI, access to greater computer processing...
- Data Story
This is part of a series of articles showcasing examples of high-value datasets from their different thematic categories. High-value datasets are defined by EU law based on their potential to provide essential benefits to society, the environment and the economy. This series aims to help readers find reliable and accurate information from official sources relating to the availability of various...
