High-value datasets – tourism in the EU
Discover statistics to analyse tourism flows
This is part of a series of articles showcasing examples of high-value datasets from their different thematic categories. High-value datasets are defined by EU law based on their potential to provide essential benefits to society, the environment and the economy. This series aims to help readers find reliable and accurate information from official sources relating to the availability of various high-value datasets, and to present this information through data visualisation. You can check out the article providing an overview of high-value datasets.
Only datasets specifically defined by law can be considered high-value datasets and, as such, the data presented in this series of articles does not necessarily fall under that definition. Instead, the data has been chosen to be thematically adjacent to high-value datasets and to showcase what can be done with information made available by official EU bodies and EU Member States. The official list of high-value datasets adopted on 12 December 2022 can be found in the legal documents that define these datasets and their characteristics.
Using high-value datasets to analyse tourism
Representing nearly 10 % of the EU’s GDP and accounting for 23 million jobs in 2019, tourism is an essential part of the EU’s economy. The EU’s tourism ecosystem involves various sectors such as food and beverage services, online information and services, travel agents and tour operators, accommodation suppliers and transportation.
Furthermore, the EU’s industrial strategy aims to accelerate the green and digital transitions and increase tourism resilience. In February 2022, the European Commission proposed a transition pathway for the tourism industry, including 27 areas of measures for the green and digital transitions and improving tourism resilience. Based on the Commission’s transition pathway, the Council of the European Union has adopted the European agenda for tourism 2030, which includes a multiannual work plan with actions for Member States, the Commission and tourism stakeholders.
In this context, data on tourism can provide essential insights and as such, tourism statistics have been included in the list of high-value datasets. The ‘Statistics’ category of high-value datasets includes several datasets about tourism flows in Europe, as laid out by section 2 of Annex I to Regulation (EU) No 692/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council.
Tourism-related high-value datasets contain information about yearly tourism flows and include indicators such as the number of nights spent at tourist establishments, including specifically by EU residents, participation in tourism for personal purposes, tourism trips and expenditures. The indicators may also offer several breakdowns, including the countries of origin and destination, duration of the trip, means of transport and accommodation. In some cases, geographical information is also accessible, with data available up to the NUTS 2 (region), NUTS 3 (province) or coastal/non-coastal area levels.
Tourism data from Eurostat
The EU’s official statistical office, Eurostat, offers a large number of datasets to study tourism, along with a detailed page in the ‘Statistics Explained’ section that shows major trends. One way to look at tourism is to analyse where people tend to come from and where they go. Eurostat data can be used to determine the countries in which people travel the most and others where tourism is less frequent.
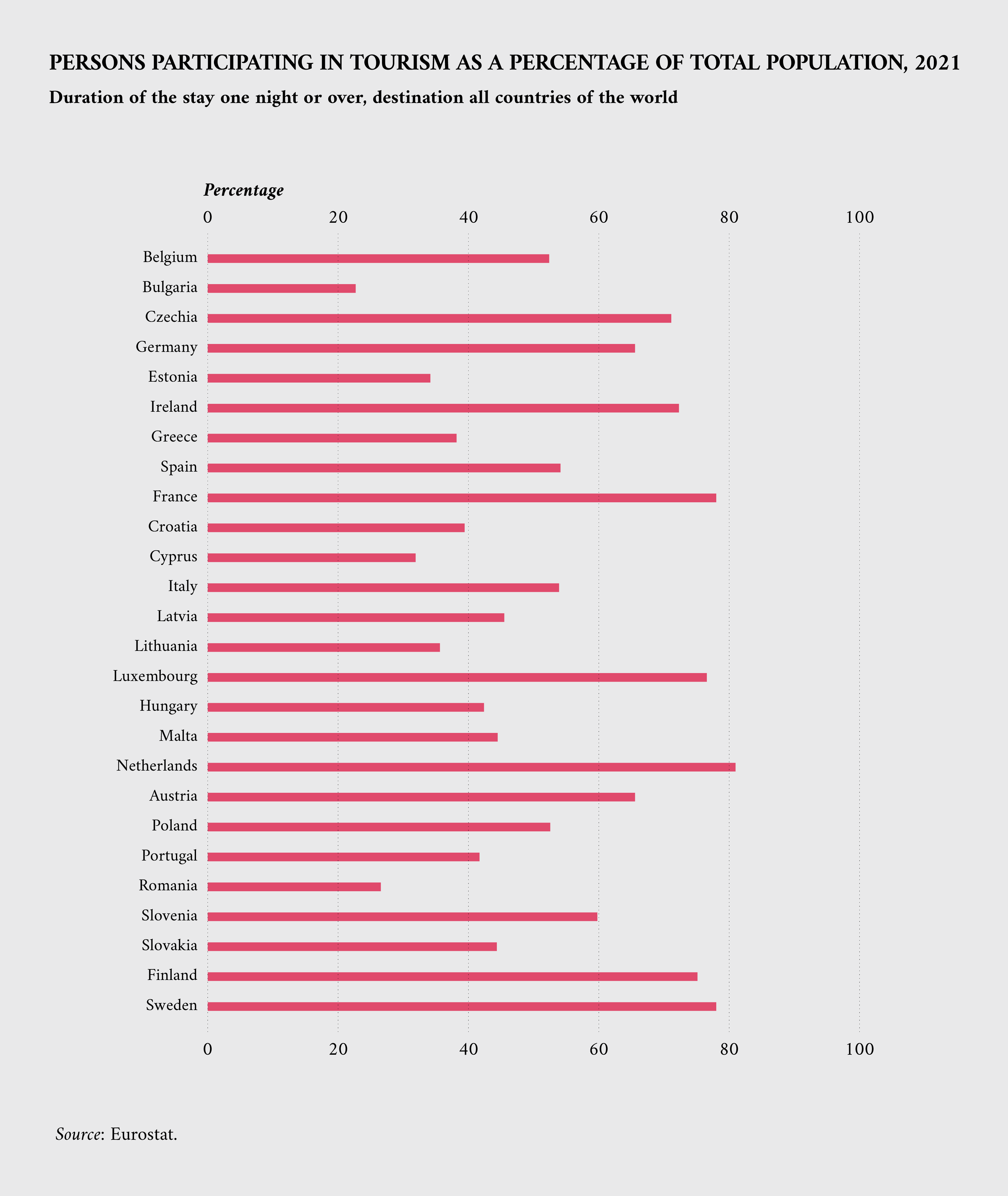
The following visualisation shows the share of people out of the total population participating in tourism, from Member States to other world destinations. This data shows that the countries with the highest values are the Netherlands, France, Luxembourg, Finland and Sweden.
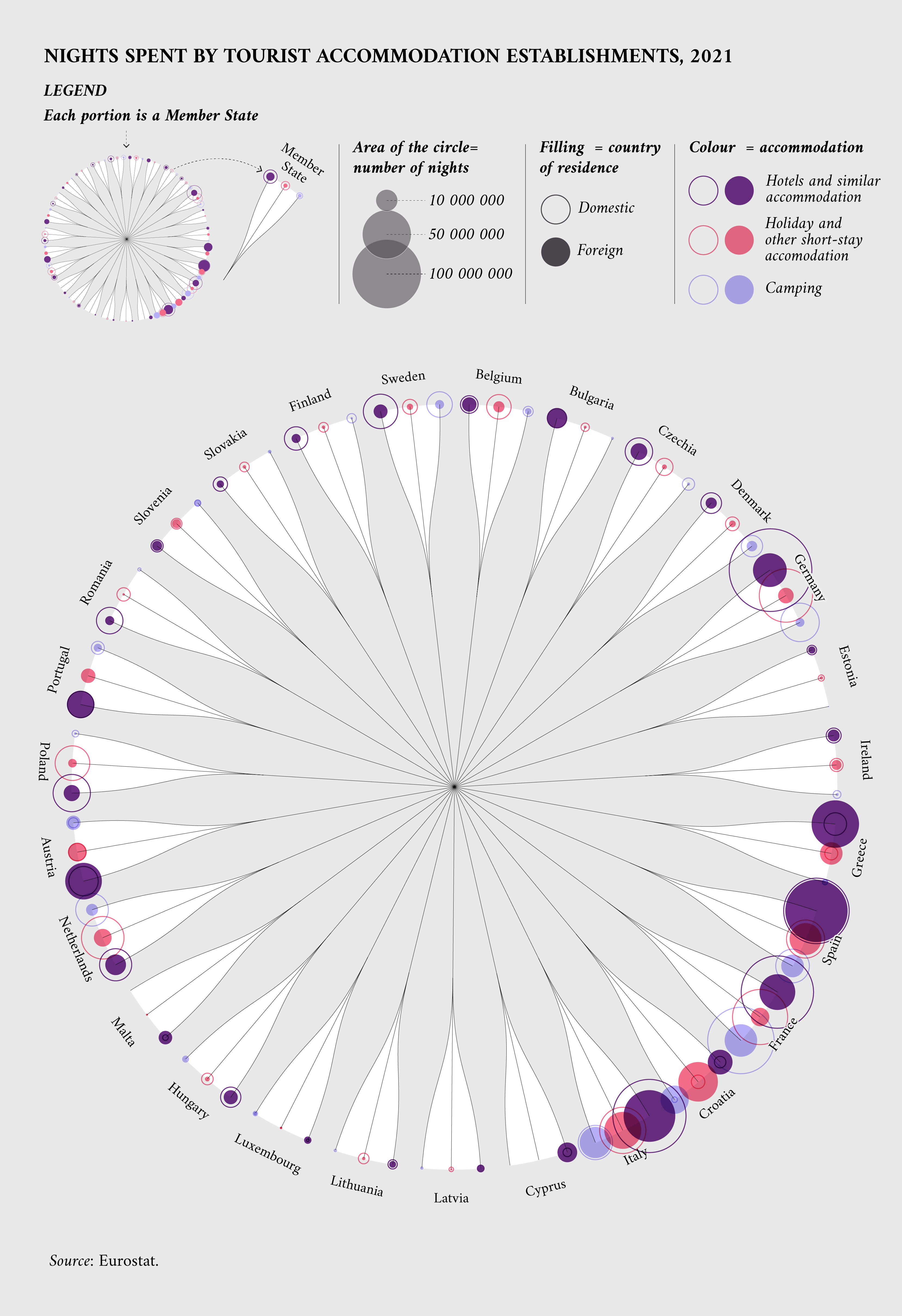
Eurostat also offers datasets that show the preferred destinations for tourists from inside and outside the EU. A good indicator to measure this phenomenon is the total number of nights spent in tourist accommodation establishments, which is available for all guests or only for international guests.
To better understand tourists’ preferences, data can be disaggregated to show the type of accommodation they chose – a hotel, a camping site or other short-term accommodation – and whether the tourists were domestic or came from abroad.
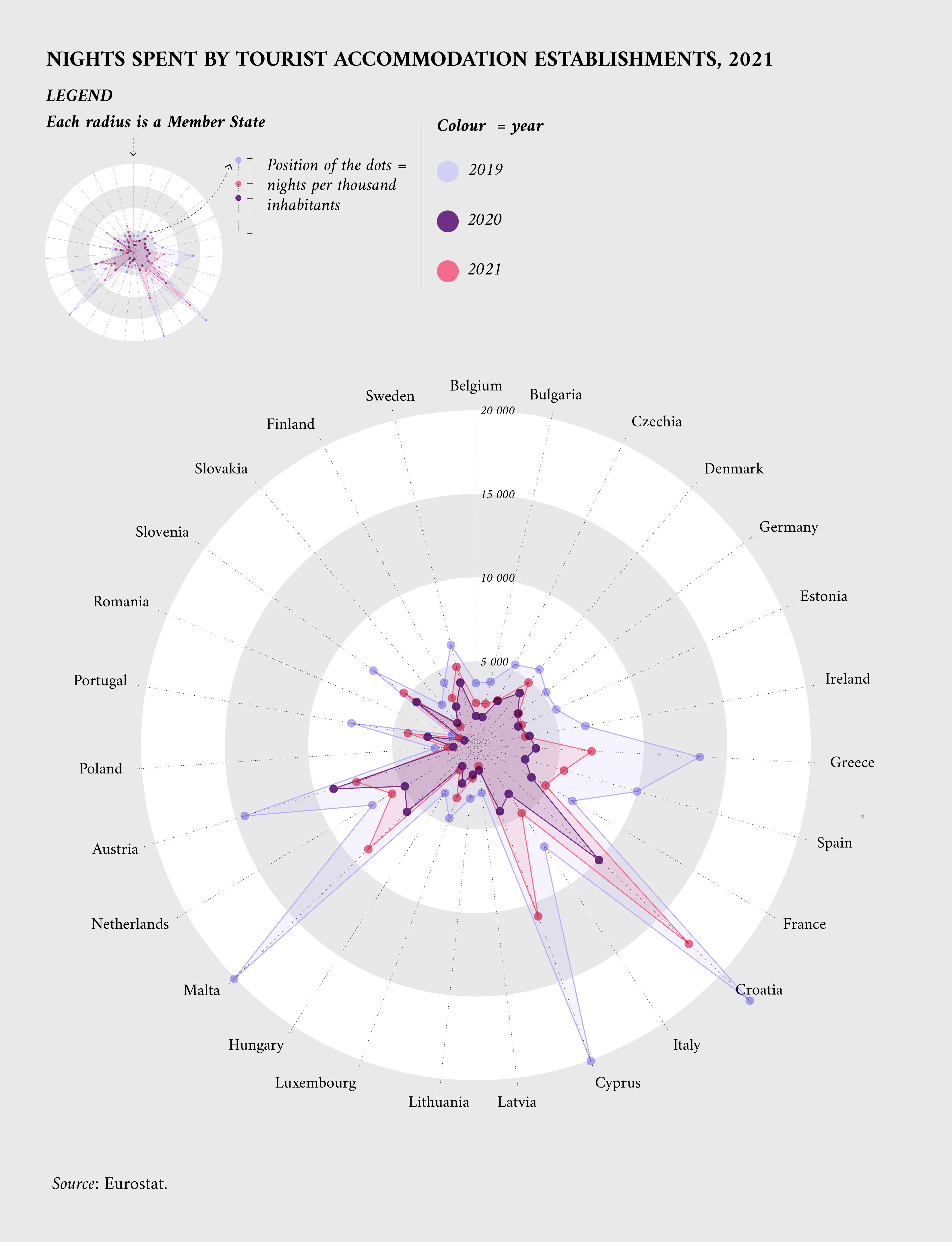
By adjusting for population, the indicator called ‘Tourism intensity’ represents the number of nights spent by domestic or international guests in tourist accommodation. Looking at this indicator, smaller countries like Croatia, Malta, Cyprus, Austria and Greece stand out as major tourism destinations.
Tourism data on data.europa.eu
As previously mentioned, high-value datasets include several indicators through which it is possible to analyse tourism from different perspectives. Information of similar scope has been provided by Member States on the data.europa.eu portal, where it can be freely reused by everyone.
One of these indicators is tourism expenditure, for which the portal provides several datasets. Examples include a study from the EU’s Joint Research Centre that estimated the average economic value generated for each night spent or a dataset showing expenditures and earnings by and from travellers to and from Ireland.
Another interesting dataset was uploaded by the data portal of the Dutch government. The Eurostat data revealed that Dutch people are among the most active in tourist activities and this dataset offers many insights about their travel habits over time.
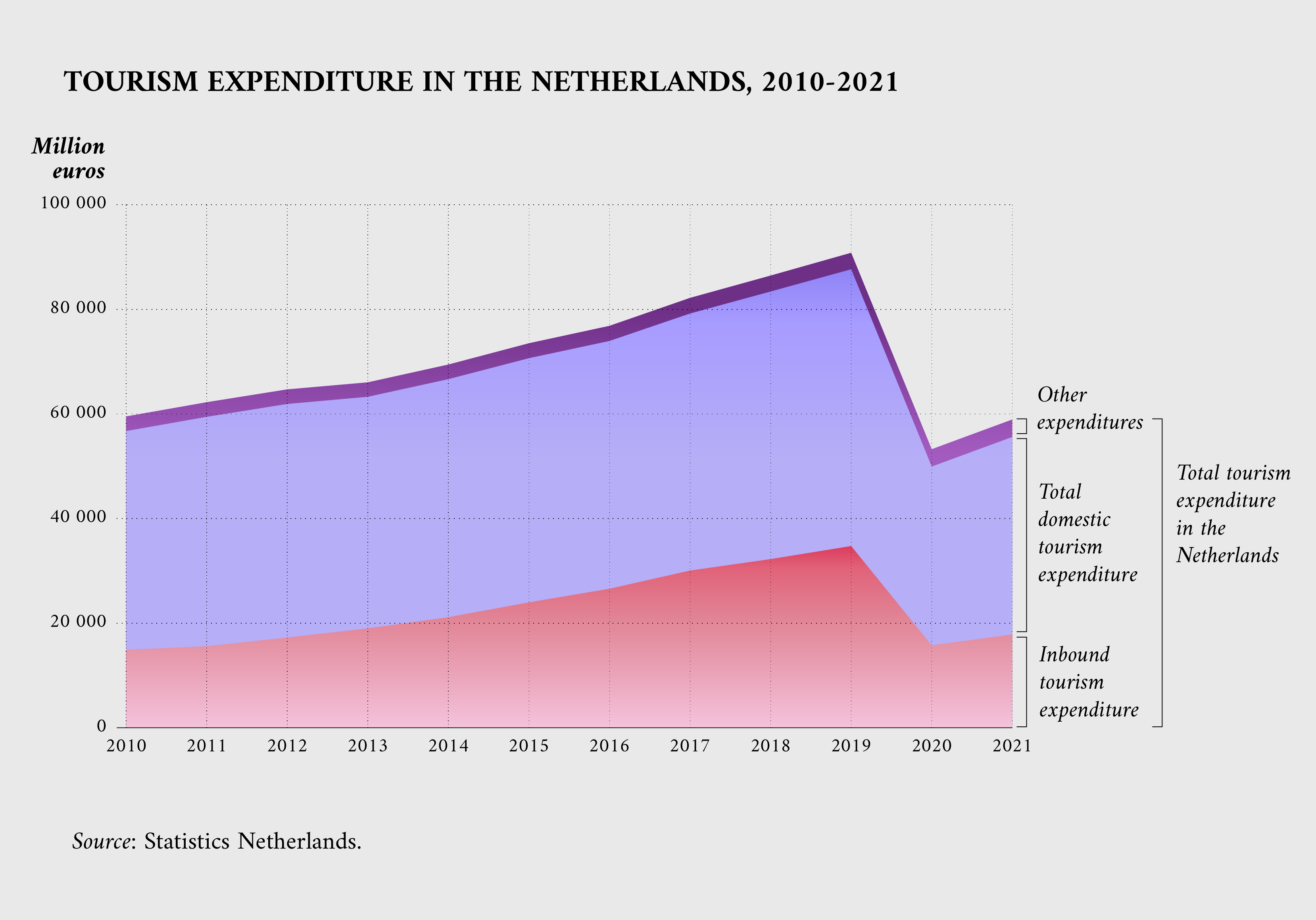
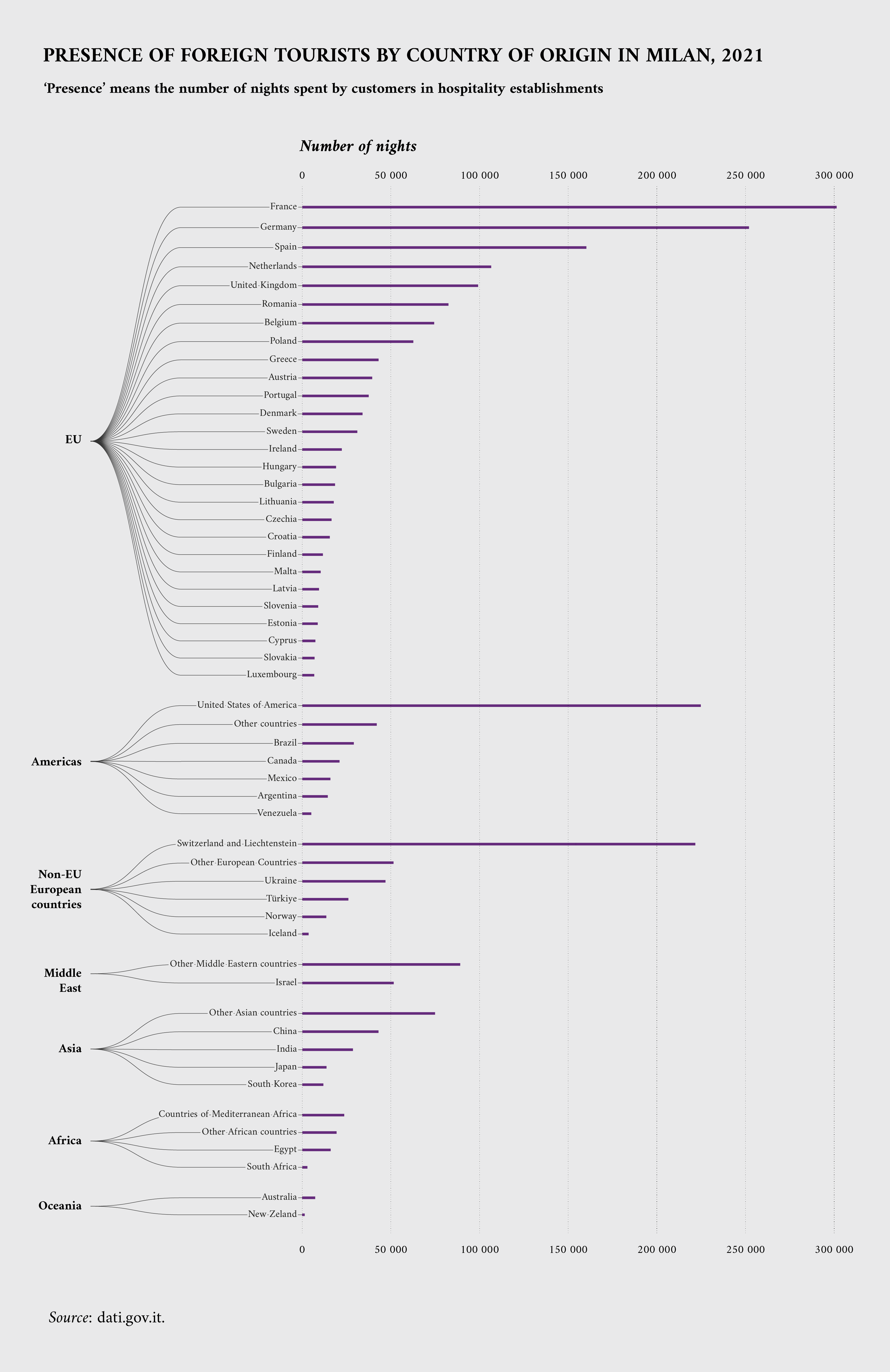
Datasets on data.europa.eu also cover other aspects related to tourism, such as means of transport, accommodation and booking modalities. Examples include a Joint Research Centre study that estimated the percentage of travel by train and the number of foreign tourists staying in Milan by area of origin and type of accommodation.
Data for tourism in Milan accounts for the number of nights spent in the city and shows a significant presence of tourists from other Member States – especially France and Germany. The third-largest influx of tourists come from the United States, while other important groups of people travelled to Milan from Switzerland, Liechtenstein and from several Middle Eastern countries.
Other than Eurostat and the Member States, data about tourism is also produced by the European Environmental Agency, which focuses on the environmental impact of tourism. Sociological data is made available by Eurobarometer, with public opinion surveys on a range of EU-related topics across its Member States regularly conducted by the Commission and other EU institutions since 1973. Some of those surveys asked European residents about their attitude towards tourism and the results can be downloaded from the data.europa.eu portal.
Download the data visualisations presented in this story and the data behind them.
Article by Davide Mancino
Data visualisations by Federica Fragapane
